 |
RML
1.0
Robotics Mathematical Library
|
 |
RML
1.0
Robotics Mathematical Library
|
Types and algorithms for robotic mobile manipulation. More...
Namespaces | |
| namespace | FrameID |
Classes | |
| class | ArmModel |
| Arm Model class for serial kinematic chains (manipulators). More... | |
| class | ArmModelJointException |
| Exception to be thrown when setting joint variable of wrong size. More... | |
| class | ArmModelNotInitializedException |
| Exception to be thrown when setting joint variable on a not initialized arm model. More... | |
| class | BaxterLeftArmModel |
| class | BellShapeParameterException |
| FUNCTIONS. More... | |
| class | EulerRPY |
| Euler RPY angle representation. More... | |
| class | ExceptionWithHow |
| class | LabelSyntaxException |
| class | NewtonEuler |
| Implementation of the Newton-Euler equation for rigid-body chains. More... | |
| struct | PlaneParameters |
| Using four parameters represention in the form: Ax + By + Cz + D = 0;. More... | |
| struct | RegularizationData |
| Regularization parameters and results container. More... | |
| struct | RegularizationParameters |
| struct | RegularizationResults |
| class | RobotLink |
| Basic element of an ArmModel. More... | |
| class | RobotModel |
| Robot Model class, to evaluate either mobile or fixed manipulators total transformation matrices and jacobians. More... | |
| class | RobotModelArmException |
| Exception to be thrown in robot model when dealing with the arm model. More... | |
| class | RobotModelWrongControlSizeVectorException |
| Exception to be thrown when trying to set a wrong control vector. More... | |
| class | TwoLinksArmModel |
| class | VehicleModel |
| Vehicle Model base class. More... | |
| class | VehicleModelNotInitializedException |
| Exception to be thrown when the vehicle model is not initialized. More... | |
| class | WrongFrameException |
| Exception to be thrown in robot model when dealing with wrong frame id's. More... | |
| class | YouBotArmModel |
| class | YouBotVehicleModel |
Typedefs | |
| typedef std::pair< std::string, Eigen::TransformationMatrix > | IndexedTMat |
Enumerations | |
| enum class | JointType : uint8_t { Fixed , Revolute , Prismatic } |
| Used to describe the type of joint. More... | |
Functions | |
| Eigen::Vector3d | ReducedVersorLemma (const Eigen::Vector3d &v1, const Eigen::Vector3d &v2) |
| Compute the misalignment error between two vectors. The result is the vector around which v1 has to rotate to reach v2. | |
| Eigen::Vector3d | VersorLemma (const Eigen::RotationMatrix &r1, const Eigen::RotationMatrix &r2) |
| Compute the versor lemma between the two rotation matrices. | |
| Eigen::Vector3d | VersorLemma (const EulerRPY &v1, const EulerRPY &v2) |
| Compute the versor lemma between the two rotation matrices. | |
| Eigen::Vector6d | CartesianError (const Eigen::TransformationMatrix &in1, const Eigen::TransformationMatrix &in2) |
| Compute the Cartesian error between two transformation matrices. | |
| Eigen::Vector6d | CartesianError (const Eigen::Vector6d &v1, const Eigen::Vector6d &v2) |
| Compute the Cartesian error between two transformation matrices. | |
| double | DecreasingBellShapedFunction (double xmin, double xmax, double ymin, double ymax, double x) noexcept(false) |
| A decreasing bell shaped (sigmoid) function. | |
| double | IncreasingBellShapedFunction (double xmin, double xmax, double ymin, double ymax, double x) noexcept(false) |
| An increasing bell shaped (sigmoid) function. | |
| void | SaturateScalar (double sat, double &value) |
| Saturate the scalar to a given maximum value. | |
| void | SaturateVector (const double sat, Eigen::VectorXd &vector) |
| Saturate the vector to a given maximum value applying normalization for preserving the vector direction. | |
| void | SaturateVector (const Eigen::VectorXd &upper_limits, const Eigen::VectorXd &lower_limits, Eigen::VectorXd &vect) |
| Saturate the vector within the specified limits. | |
| double | DistancePointToPlane (const Eigen::Vector3d &point, const PlaneParameters &planeParams) |
| Evaluates the norm of the shortest distance vector among a point and a given plane. | |
| Eigen::Vector3d | ClosestPointOnPlane (const Eigen::Vector3d &point, const PlaneParameters &planeParams) |
| Given a point and a plane evaluates the coordinates of the closest point on plane w.r.t the input one. | |
| Eigen::Matrix3d | Vect3ToSkew (const Eigen::Vector3d &t) |
| Computes the skew symmetric matrix form for a vector. | |
| Eigen::Matrix6d | RigidBodyMatrix (const Eigen::Vector3d &transl) |
| Compute a rigid body matrix. | |
| Eigen::MatrixXd | ChangeJacobianObserver (Eigen::MatrixXd J, Eigen::MatrixXd Jobserver, Eigen::Vector3d CartesianError) |
| ChangeJacobianObserver Method implementing change of observer for a cartesian Jacobian. . | |
| template<class MatT > | |
| MatT | GreatestNormElement (const MatT &vect1, const MatT &vect2, const MatT &vect3) |
| An utility to find the vector with the greatest norm among three. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| int | sgn (T val) |
| void | Double2Matrix (double dmat[], int rows, int cols, Eigen::MatrixXd &MatT) |
| void | Matrix2Double (const Eigen::MatrixXd &MatT, int rows, int cols, double dmat[]) |
| void | Double2Vector (double dmat[], int rows, Eigen::VectorXd &MatT) |
| void | Vector2Double (const Eigen::VectorXd &MatT, int rows, double dmat[]) |
| void | SetDiagonalFromDouble (Eigen::MatrixXd &MatT, double diag[]) |
| Eigen::MatrixXd | RightJuxtapose (const Eigen::MatrixXd &A, const Eigen::MatrixXd &B) |
| Eigen::MatrixXd | UnderJuxtapose (const Eigen::MatrixXd &A, const Eigen::MatrixXd &B) |
| void | RegPinv (const double *J, int m, int n, double *JPInv, double treshold, double lambda, double *prod, int *flag) |
| template<class MatT > | |
| Eigen::Matrix< typename MatT::Scalar, MatT::ColsAtCompileTime, MatT::RowsAtCompileTime > | RegularizedPseudoInverse (const MatT &mat, RegularizationData ®Data) |
| Computes the SVD-based regularized matrix pseudoinversion (A = U*S*V') | |
| void | SVD_NumericalRecipes (double *a, int m, int n, double *w, double *v, double *rv1) |
| template<class MatT > | |
| void | SVD (const MatT &A, MatT &U, MatT &S, MatT &V) |
| Singular Value Decomposition. | |
| double | RaisedCosine (double in, double th, double lambda) |
| short | MatrixMultiply (const double *A, int m, int n, const double *B, char k, char p, double *OUT) |
| void | MatrixTranspose (const double *A, int m, int n, double *OUT) |
| double | SmoothTransition (double x, double beta, double xmin, double lambda) |
| double | SmoothFunction (double x, double beta, double lambda) |
Variables | |
| const double | STD_GRAVITY = 9.80665 |
| const std::map< JointType, std::string > | JointType2String |
| const double | RPY2VectEpsilon = 0.000000001 |
| const unsigned long int | MaxMatrixDim = 1300 |
| Max matrices dimension. | |
| const double | SVDEpsilon = 0.00000001 |
Types and algorithms for robotic mobile manipulation.
The "Robotic Mathematical Library" is a minimal and portable math lib for robotics that relies on Eigen. It includes tools for matrix pseudo inversion and the SVD algorithm. It also provides utility functions for type conversion and data extraction for transformation and rotation matrices, RPY angle representation, rigid body matrices and matrix juxtaposition.
Types:
Structs:
Strong Enums:
Classes:
Functions:
| typedef std::pair<std::string, Eigen::TransformationMatrix> rml::IndexedTMat |
|
strong |
| Eigen::Vector6d rml::CartesianError | ( | const Eigen::TransformationMatrix & | in1, |
| const Eigen::TransformationMatrix & | in2 | ||
| ) |
Compute the Cartesian error between two transformation matrices.
The method computes the misalignment error and the position error between two transformation matrices It uses the VersorLemma to compute the misalignment, and a simple difference to compute the linear distance The result is the error that brings in1 towards in2
| [in] | in1 | the initial transformation matrix |
| [in] | in2 | the goal transformation matrix |
| Eigen::Vector6d rml::CartesianError | ( | const Eigen::Vector6d & | v1, |
| const Eigen::Vector6d & | v2 | ||
| ) |
Compute the Cartesian error between two transformation matrices.
The method computes the misalignment error and the position error between two transformation matrices expressed as their 6 parameters representation The method assumes that the two Vect6 are a 6 parameter representation of the type v = [yaw pitch roll x y z] leading to the following rotational part R = Rz(yaw) * Ry(pitch) * Rx(roll) It uses the VersorLemma to compute the misalignment, and a simple difference to compute the linear distance The result is the error that brings in1 towards in2
| [in] | v1 | the initial transformation matrix expressed as its 6 parameter representation |
| [in] | v2 | the goal transformation matrix expressed as its 6 parameter representation |
| Eigen::MatrixXd rml::ChangeJacobianObserver | ( | Eigen::MatrixXd | J, |
| Eigen::MatrixXd | Jobserver, | ||
| Eigen::Vector3d | CartesianError | ||
| ) |
ChangeJacobianObserver Method implementing change of observer for a cartesian Jacobian.
.
![]()
| J | error jacobian wrt to the inertial frame |
| Jobserver | jacobian of the observer wrt to the inertial frame |
| CartesianError | error |
| Eigen::Vector3d rml::ClosestPointOnPlane | ( | const Eigen::Vector3d & | point, |
| const PlaneParameters & | planeParams | ||
| ) |
Given a point and a plane evaluates the coordinates of the closest point on plane w.r.t the input one.
| [in] | point | The point from where calculate the distance |
| [in] | planeParams | The target plane |
| double rml::DecreasingBellShapedFunction | ( | double | xmin, |
| double | xmax, | ||
| double | ymin, | ||
| double | ymax, | ||
| double | x | ||
| ) |
A decreasing bell shaped (sigmoid) function.
The output of this function has a smooth behavior, starting from the value (xmin, ymax) to (xmax, ymin) For ![]()
For ![]()
| [in] | xmin | the lower extreme value where the transition begins |
| [in] | xmax | the higher extreme value where the transition stops |
| [in] | ymin | the lowest value of the function |
| [in] | ymax | the highest value of the function |
| [in] | x | the value where the function is evaluated |
| double rml::DistancePointToPlane | ( | const Eigen::Vector3d & | point, |
| const PlaneParameters & | planeParams | ||
| ) |
Evaluates the norm of the shortest distance vector among a point and a given plane.
| [in] | point | The point from where calculate the distance |
| [in] | planeParams | The target plane |
|
inline |
|
inline |
| MatT rml::GreatestNormElement | ( | const MatT & | vect1, |
| const MatT & | vect2, | ||
| const MatT & | vect3 | ||
| ) |
An utility to find the vector with the greatest norm among three.
| vect1 | |
| vect2 | |
| vect3 |
| double rml::IncreasingBellShapedFunction | ( | double | xmin, |
| double | xmax, | ||
| double | ymin, | ||
| double | ymax, | ||
| double | x | ||
| ) |
An increasing bell shaped (sigmoid) function.
The output of this function has a smooth behavior, starting from the value (xmin, ymin) to (xmax, ymax)
For ![]()
For ![]()
| [in] | xmin | the lower extreme value where the transition begins |
| [in] | xmax | the higher extreme value where the transition stops |
| [in] | ymin | the lowest value of the function |
| [in] | ymax | the highest value of the function |
| [in] | x | the value where the function is evaluated |
|
inline |
| short rml::MatrixMultiply | ( | const double * | A, |
| int | m, | ||
| int | n, | ||
| const double * | B, | ||
| char | k, | ||
| char | p, | ||
| double * | OUT | ||
| ) |
| void rml::MatrixTranspose | ( | const double * | A, |
| int | m, | ||
| int | n, | ||
| double * | OUT | ||
| ) |
| double rml::RaisedCosine | ( | double | in, |
| double | th, | ||
| double | lambda | ||
| ) |
| Eigen::Vector3d rml::ReducedVersorLemma | ( | const Eigen::Vector3d & | v1, |
| const Eigen::Vector3d & | v2 | ||
| ) |
Compute the misalignment error between two vectors. The result is the vector around which v1 has to rotate to reach v2.
| [in] | v1 | first orientation vector |
| [in] | v2 | second orientation vector |
| void rml::RegPinv | ( | const double * | J, |
| int | m, | ||
| int | n, | ||
| double * | JPInv, | ||
| double | treshold, | ||
| double | lambda, | ||
| double * | prod, | ||
| int * | flag | ||
| ) |
| Eigen::Matrix< typename MatT::Scalar, MatT::ColsAtCompileTime, MatT::RowsAtCompileTime > rml::RegularizedPseudoInverse | ( | const MatT & | mat, |
| RegularizationData & | regData | ||
| ) |
Computes the SVD-based regularized matrix pseudoinversion (A = U*S*V')
The regularization, being ![]() the i-th singular value, is performed using following formula:
the i-th singular value, is performed using following formula:
![]() , where, using the raised cosine
, where, using the raised cosine
![]()
| mat | The matrix to be inverted |
| regData | The regularization parameters and results struct |
mat
|
inline |
| Eigen::Matrix6d rml::RigidBodyMatrix | ( | const Eigen::Vector3d & | transl | ) |
Compute a rigid body matrix.
This method assumes that the three values stored in the Vect3 correspond to a translation r between two frames Then it computes the rigid body transformation matrix defined as
![]()
| void rml::SaturateScalar | ( | double | sat, |
| double & | value | ||
| ) |
Saturate the scalar to a given maximum value.
| [in] | sat | the value of the saturation |
| [in,out] | value | the value which is saturated to the maximum value |
| void rml::SaturateVector | ( | const double | sat, |
| Eigen::VectorXd & | vector | ||
| ) |
Saturate the vector to a given maximum value applying normalization for preserving the vector direction.
| [in] | sat | the value of the saturation |
| [in,out] | vector | the vector which is saturated to the maximum value |
| void rml::SaturateVector | ( | const Eigen::VectorXd & | upper_limits, |
| const Eigen::VectorXd & | lower_limits, | ||
| Eigen::VectorXd & | vect | ||
| ) |
Saturate the vector within the specified limits.
This function ensures that all components of a given vector remain within the bounds defined by the provided upper and lower limits. If any component of the vector exceeds its corresponding upper limit or falls below its lower limit, the entire vector is scaled proportionally to keep all components within the valid range.
The scaling process ensures that the direction of the vector is preserved while bringing all components within bounds. The scaling factor is calculated based on the strictest limit violation across all components.
| [in] | upper_limits | The upper limits for each component of the vector. This must be the same size as the input vector. |
| [in] | lower_limits | The lower limits for each component of the vector. This must be the same size as the input vector. |
| [in,out] | vect | The vector to be saturated. This vector is updated in place to ensure all its components lie within the specified bounds. |
upper_limits or lower_limits vectors does not match the size of the input vect, the function will throw a std::invalid_argument exception.| std::invalid_argument | If the size of the upper_limits or lower_limits does not match the size of vect. |
|
inline |
| int rml::sgn | ( | T | val | ) |
| double rml::SmoothFunction | ( | double | x, |
| double | beta, | ||
| double | lambda | ||
| ) |
| double rml::SmoothTransition | ( | double | x, |
| double | beta, | ||
| double | xmin, | ||
| double | lambda | ||
| ) |
| void rml::SVD | ( | const MatT & | A, |
| MatT & | U, | ||
| MatT & | S, | ||
| MatT & | V | ||
| ) |
Singular Value Decomposition.
The methods computes the singular value decomposition of the given matrix A, defined as A = USV'. If A is of size m x n, then U is m x m, S is m x n and V is n x n
| [in] | A | the matrix to be decomposed |
| [out] | U | the m x m rotation matrix |
| [out] | S | the m x n singular values matrix |
| [out] | V | the n x n rotation matrix |
| void rml::SVD_NumericalRecipes | ( | double * | a, |
| int | m, | ||
| int | n, | ||
| double * | w, | ||
| double * | v, | ||
| double * | rv1 | ||
| ) |
|
inline |
| Eigen::Matrix3d rml::Vect3ToSkew | ( | const Eigen::Vector3d & | t | ) |
Computes the skew symmetric matrix form for a vector.
The output is the following:
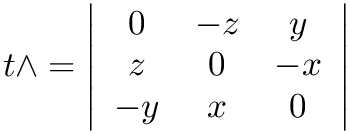
| t | input vector |
|
inline |
| Eigen::Vector3d rml::VersorLemma | ( | const Eigen::RotationMatrix & | r1, |
| const Eigen::RotationMatrix & | r2 | ||
| ) |
Compute the versor lemma between the two rotation matrices.
Computes the misalignment vector between the two frames, represented by the two rotation matrices The vector is the axis around which the first frame should rotate in order to become equal to the second (angle-axis representation)
| [in] | r1 | the first rotation matrix |
| [in] | r2 | the second rotation matrix |
Compute the versor lemma between the two rotation matrices.
Computes the misalignment vector between the two frames, represented by the two rotation matrices expressed as their RPY representation In particular, both v1 and v2 are assumed to be in the form: [yaw -pitch roll] giving the following matrix R = Rz(yaw) * Ry(pitch) * Rx(roll) The vector is the axis around which the first frame should rotate in order to become equal to the second (angle-axis representation).
| [in] | v1 | the RPY representation of the first rotation matrix |
| [in] | v2 | the RPY representation of the second rotation matrix |
| const std::map<JointType, std::string> rml::JointType2String |
| const unsigned long int rml::MaxMatrixDim = 1300 |
Max matrices dimension.
| const double rml::RPY2VectEpsilon = 0.000000001 |
| const double rml::STD_GRAVITY = 9.80665 |
| const double rml::SVDEpsilon = 0.00000001 |